Spark supports the processing of reagents into searchable databases. To take advantage of this feature you will need a Spark Database Generator License. The currently available processing rules are listed below.
Additional rules can be created and easily deployed to meet your needs. Contact Cresset support if a suitable rule is not listed or to discuss reagent creation rules.
| Transformation | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acids, delete the -COOH | Acids/acid chlorides where we keep only the group attached to the acid carbonyl. e.g. R-COOH -> R-* |
 |
Acids, keep the CO | Acids/acid chlorides, where we attach through the carbonyl group (eg acylations) e.g. R-COOH -> R-C(=O)-* |
 |
Alcohols, keep the O | Alcohols and phenols where the attachment is through the oxygen e.g. R-OH -> R-O-* |
 |
Aldehydes/ketones, delete the O and reduce C | Aldehydes/ketones where we attach through reductive amination e.g. R1-C(=O)-R2 -> R1-CH(R2)-* |
 |
Aliphatic alcohols, delete the O | Aliphatic alcohols used as alkylating agents where the O is deleted on addition e.g. R-OH -> R-* |
 |
Aliphatic halide | Primary/secondary/tertiary aliphatic halides (Cl,Br,I) e.g. R(1-3)C-Cl -> R(1-3)C-* |
 |
Aliphatic thiols, delete S | Thiols used as alkylating agents where the S is deleted on addition e.g. R-SH -> R-* |
 |
Alkynes, delete the -C#C | Alkynes, keep only the attached group e.g. R-C#C -> R-* |
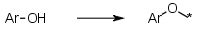 |
Aromatic alcohols, keep the O | Aromatic alcohols (phenols) where the attachment is through the oxygen e.g. Ar-OH -> Ar-O-* |
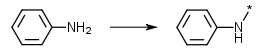 |
Aromatic amines, keep the N | Primary and secondary aromatic amines (anilines) where the N is the attachment point such as in reductive aminations e.g. Ar-NH-R -> Ar-N(-R)-* |
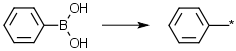 |
Aromatic boronic acids, delete -B(OH)2 | Aromatic boronic acids for Suzuki couplings etc: lose the boronic acid and attach the remainder e.g. Ph-B(OH)2 -> Ph-* |
 |
Aromatic halide | Aromatic halides (Cl,Br,I) e.g. Ph-Cl -> Ph-* |
 |
Cyano groups, delete -CN | Cyano reagents, keeping only the attached group e.g. R-CN -> R-* |
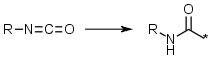 |
Isocyanates, keep -NCO | Isocyanates, keeping all atoms and forming an amide e.g. R-N=C=O -> R-N-C(=O)-* |
 |
Olefins, delete the -C=C | Terminal olefins, keep only the attached group e.g. R-C=C -> R-* |
 |
Primary aliphatic amines, delete the N | Primary aliphatic amines as an alkylating agent where the N is deleted on addition e.g. R-NH2 -> R-* |
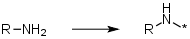 |
Primary aliphatic amines, keep the N | Primary aliphatic amines where the N is the attachment point such as in reductive aminations e.g. R-NH2 -> R-NH-* |
 |
Primary aliphatic halide | Primary aliphatic halides (Cl,Br,I) e.g. R-CH2-Cl -> R-CH2-* |
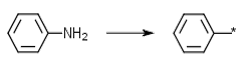 |
Primary aromatic amines, delete N | Primary aromatic amines (anilines) where the N is removed e.g. Ar-NH2 -> Ar-* |
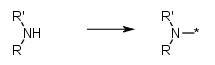 |
Secondary aliphatic amines, keep the N | Secondary aliphatic amines where the N is the attachment point such as in nucleophilic substitution e.g. R1(R2)NH -> R1(R2)N-* |
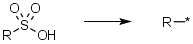 |
Sulfonic acids, delete the -SO2X | Sulfonic acids/acid chlorides where we keep only the group attached to the sulfur e.g. R-SO3H -> R-* |
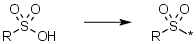 |
Sulfonic acids, keep the -SO2 | Sulfonic acids/acid chlorides where we keep the -SO2 group e.g. R-SO3H -> R-SO2-* |
 |
Thiols, keep the S | Thiols where the attachment is through the sulfur e.g. R-SH -> R-S-* |